Page 252 - A Practical Guide from Design Planning to Manufacturing
P. 252
224 Chapter Seven
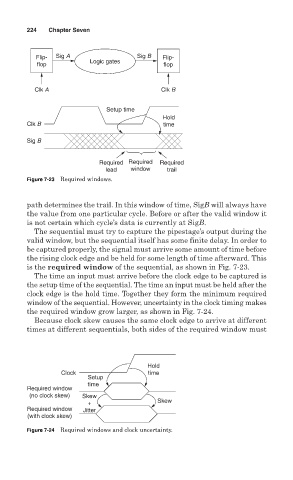
Flip- Sig A Sig B Flip-
flop Logic gates flop
Clk A Clk B
Setup time
Hold
Clk B time
Sig B
Required Required Required
lead window trail
Figure 7-23 Required windows.
path determines the trail. In this window of time, SigB will always have
the value from one particular cycle. Before or after the valid window it
is not certain which cycle’s data is currently at SigB.
The sequential must try to capture the pipestage’s output during the
valid window, but the sequential itself has some finite delay. In order to
be captured properly, the signal must arrive some amount of time before
the rising clock edge and be held for some length of time afterward. This
is the required window of the sequential, as shown in Fig. 7-23.
The time an input must arrive before the clock edge to be captured is
the setup time of the sequential. The time an input must be held after the
clock edge is the hold time. Together they form the minimum required
window of the sequential. However, uncertainty in the clock timing makes
the required window grow larger, as shown in Fig. 7-24.
Because clock skew causes the same clock edge to arrive at different
times at different sequentials, both sides of the required window must
Hold
Clock time
Setup
time
Required window
(no clock skew) Skew
+ Skew
Required window Jitter
(with clock skew)
Figure 7-24 Required windows and clock uncertainty.