Page 113 - Microsensors, MEMS and Smart Devices - Gardner Varadhan and Awadelkarim
P. 113
94 STANDARD MICROELECTRONIC TECHNOLOGIES
Gate (G)
Source (S)
JFET depletion type
(b)
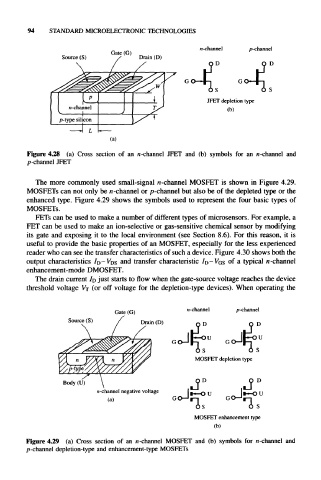
Figure 4.28 (a) Cross section of an n-channel JFET and (b) symbols for an n-channel and
p-channel JFET
The more commonly used small-signal n-channel MOSFET is shown in Figure 4.29.
MOSFETs can not only be n-channel or p-channel but also be of the depleted type or the
enhanced type. Figure 4.29 shows the symbols used to represent the four basic types of
MOSFETs.
FETs can be used to make a number of different types of microsensors. For example, a
FET can be used to make an ion-selective or gas-sensitive chemical sensor by modifying
its gate and exposing it to the local environment (see Section 8.6). For this reason, it is
useful to provide the basic properties of an MOSFET, especially for the less experienced
reader who can see the transfer characteristics of such a device. Figure 4.30 shows both the
output characteristics I D-V DS and transfer characteristic I D-V GS of a typical n-channel
enhancement-mode DMOSFET.
The drain current I D just starts to flow when the gate-source voltage reaches the device
threshold voltage V T (or off voltage for the depletion-type devices). When operating the
Gate (G)
Source (S) Drain (D)
S OS
MOSFET depletion type
Body (U)
n-channel negative voltage
(a)
s 'l.
MOSFET enhancement type
(b)
Figure 4.29 (a) Cross section of an n-channel MOSFET and (b) symbols for n -channel and
p-channel depletion-type and enhancement-type MOSFETs