Page 310 - Solid Waste Analysis and Minimization a Systems Approach
P. 310
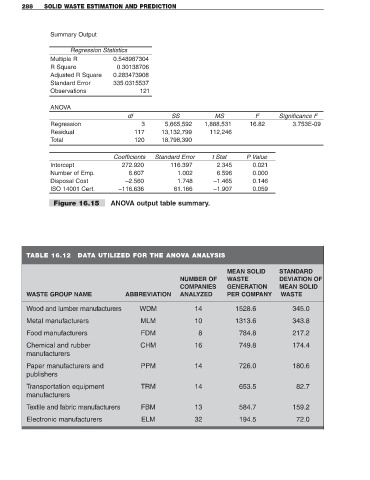
288 SOLID WASTE ESTIMATION AND PREDICTION
Summary Output
Regression Statistics
Multiple R 0.548987304
R Square 0.30138706
Adjusted R Square 0.283473908
Standard Error 335.0315537
Observations 121
ANOVA
df SS MS F Significance F
Regression 3 5,665,592 1,888,531 16.82 3.753E-09
Residual 117 13,132,799 112,246
Total 120 18,798,390
Coefficients Standard Error t Stat P Value
Intercept 272.920 116.397 2.345 0.021
Number of Emp. 6.607 1.002 6.596 0.000
Disposal Cost –2.560 1.748 –1.465 0.146
ISO 14001 Cert. –116.636 61.166 –1.907 0.059
Figure 16.15 ANOVA output table summary.
TABLE 16.12 DATA UTILIZED FOR THE ANOVA ANALYSIS
MEAN SOLID STANDARD
NUMBER OF WASTE DEVIATION OF
COMPANIES GENERATION MEAN SOLID
WASTE GROUP NAME ABBREVIATION ANALYZED PER COMPANY WASTE
Wood and lumber manufacturers WDM 14 1528.6 345.0
Metal manufacturers MLM 10 1313.6 343.8
Food manufacturers FDM 8 784.8 217.2
Chemical and rubber CHM 16 749.8 174.4
manufacturers
Paper manufacturers and PPM 14 726.0 180.6
publishers
Transportation equipment TRM 14 653.5 82.7
manufacturers
Textile and fabric manufacturers FBM 13 584.7 159.2
Electronic manufacturers ELM 32 194.5 72.0