Page 1115 - The Mechatronics Handbook
P. 1115
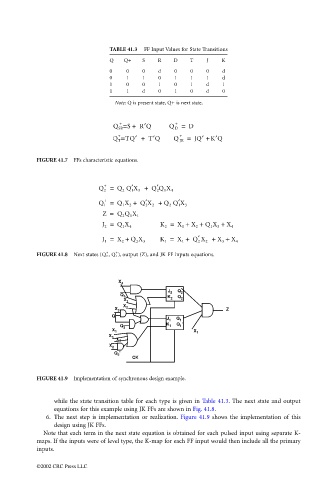
TABLE 41.3 FF Input Values for State Transitions
Q Q+ S R D T J K
0 0 0 d 0 0 0 d
0 1 1 0 1 1 1 d
1 0 0 1 0 1 d 1
1 1 d 0 1 0 d 0
Note: Q is present state, Q+ is next state.
+
+
=
Q SR S + R′Q Q D = D
+ +
=
Q T TQ′ + T′Q Q JK = JQ′ + K′Q
FIGURE 41.7 FFs characteristic equations.
′
′
+
Q 2 = Q 2 Q 1 X 3 + Q 2 Q 1 X 4
+ ′ ′
Q 1 = Q 1 X 2 + Q 2 X 2 + Q 2 Q 1 X 3
Z = Q 2 Q 1 X 1
J 2 = Q 1 X 4 K 2 = X 1 + X 2 + Q 1 X 3 + X 4
′
J 1 = X 2 + Q X 3 K 1 = X 1 + Q 2 X 2 + X 3 + X 4
2
+
+
FIGURE 41.8 Next states (Q 2 , Q 1 ) , output (Z), and JK FF inputs equations.
X 4
J 2 Q 2
Q 1
K 2 Q 2
X 1
X 2
Z
X 3
Q
J 1 Q 1
Q 1 '
K 1
Q 2
X 1
X 1
X 3
X 4
X 2
Q 2 '
CK
FIGURE 41.9 Implementation of synchronous design example.
while the state transition table for each type is given in Table 41.3. The next state and output
equations for this example using JK FFs are shown in Fig. 41.8.
6. The next step is implementation or realization. Figure 41.9 shows the implementation of this
design using JK FFs.
Note that each term in the next state equation is obtained for each pulsed input using separate K-
maps. If the inputs were of level type, the K-map for each FF input would then include all the primary
inputs.
©2002 CRC Press LLC